Supreme Tips About How To Treat Hypovolemia

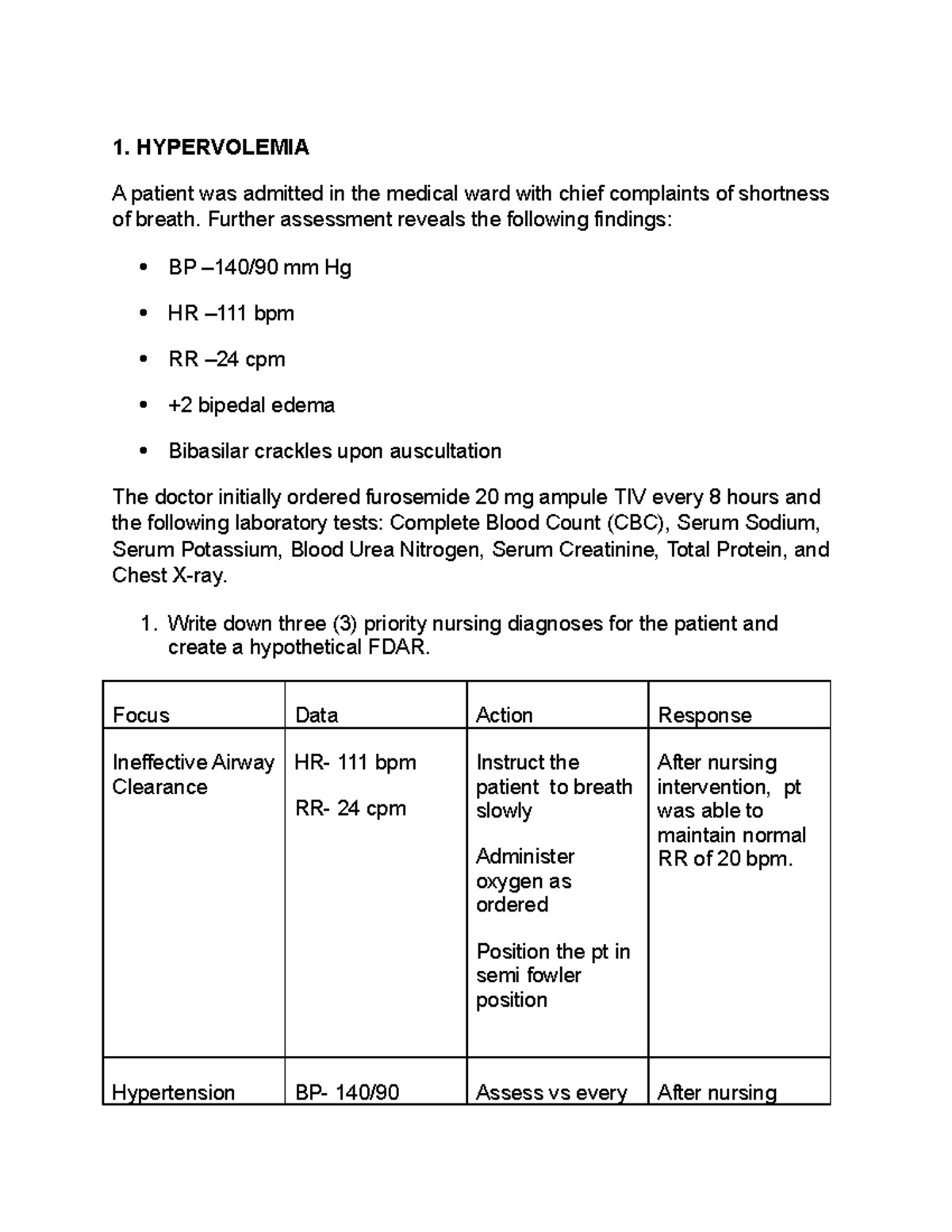
Treatment hypovolemia is the loss of 15% or more of the fluid circulating in the body, specifically blood or water.
How to treat hypovolemia. Stabilize the head and neck before moving a person with a suspected spinal injury. [1] hypovolemic shock is circulatory failure due to effective intravascular volume loss (fluids or blood). The prehospital care team should work to prevent further injury, transport the patient to the.
Because your organs need these fluids to function, their depletion can cause organs to malfunction and fail. Hypovolemic shock is a dangerous condition that happens when you suddenly lose a lot of blood or fluids from your body. Water freely travels outside the vasculature, so as little as 10% of isotonic fluid remains in the intravascular space.
Relative hypovolemia is treated primarily with fluids and vasopressors. Good sources of vitamin c include broccoli, kale, oranges, and bell peppers. Treatment in older adults outlook hypovolemic shock is a medical emergency that happens when your body loses too much blood or fluid.
They will also give you medicines to help bring your blood pressure back up to normal. Coconut water can be used to replace fluids in the body, as it is high in potassium, an electrolyte. Absolute hypovolemia is treated with fluids (e.g., crystalloids;
If person is having an allergic reaction, treat the allergic reaction, if you know how. How is hypovolemic shock treated? If the person must be carried, try to keep them flat, with the head down and feet lifted.
This effective circulatory volume loss leads to tissue hypoperfusion and tissue hypoxia. Crystalloid solutions for intravascular volume replenishment are typically isotonic (eg, 0.9% saline or ringer's lactate). How is hypovolemia diagnosed?
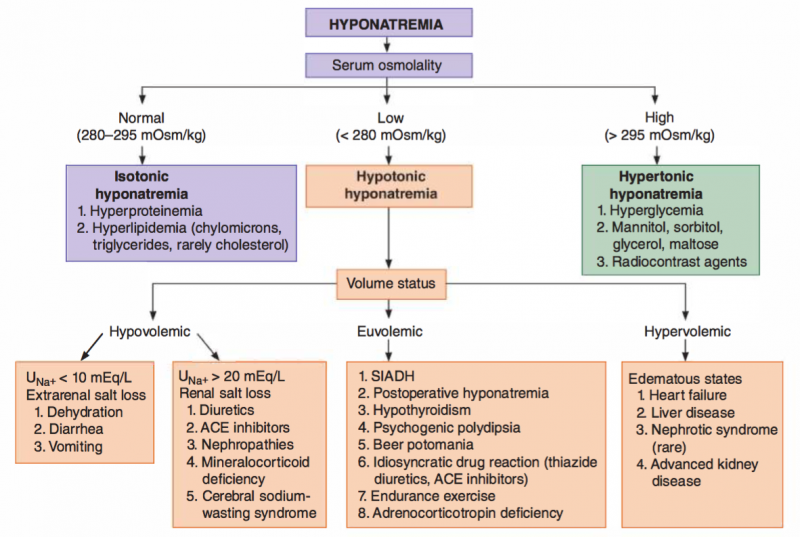
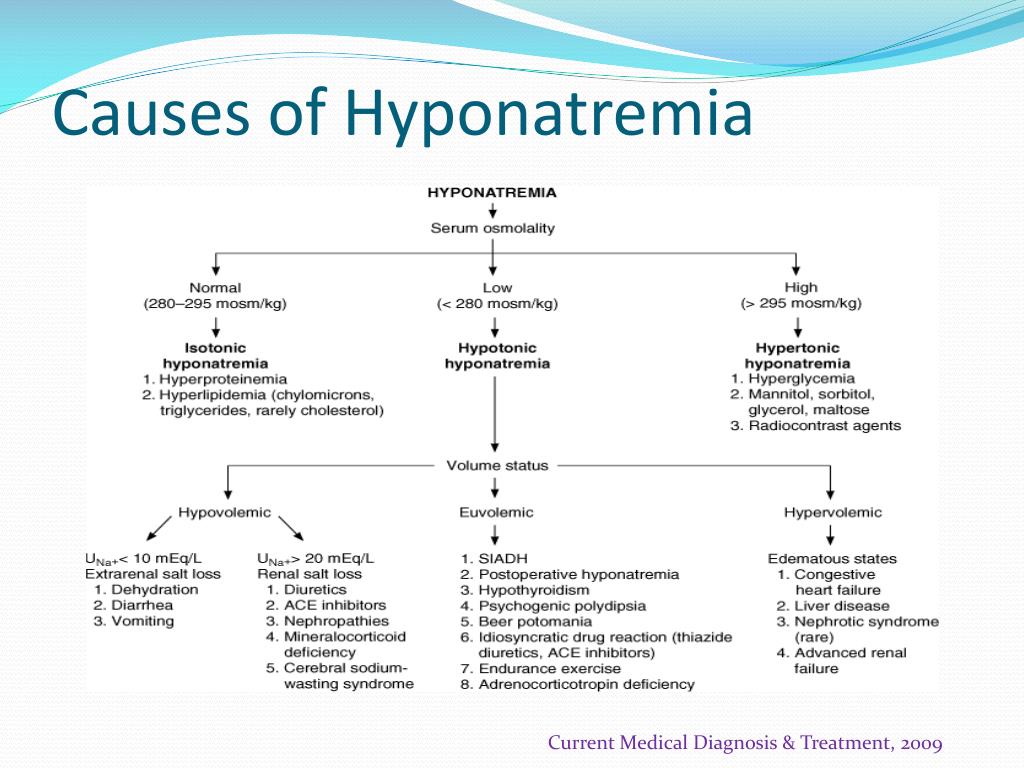
In patients with chronic hyponatremia, fluid restriction is the mainstay of treatment, with demeclocycline therapy reserved for use in persistent cases. Replace lost blood and other fluids what else helps hypovolemic shock is to replace lost blood and other fluids. Hypovolemia is a sign of an underlying disorder, therefore, consultations should be tailored to the disease that is causing the hypovolemia.
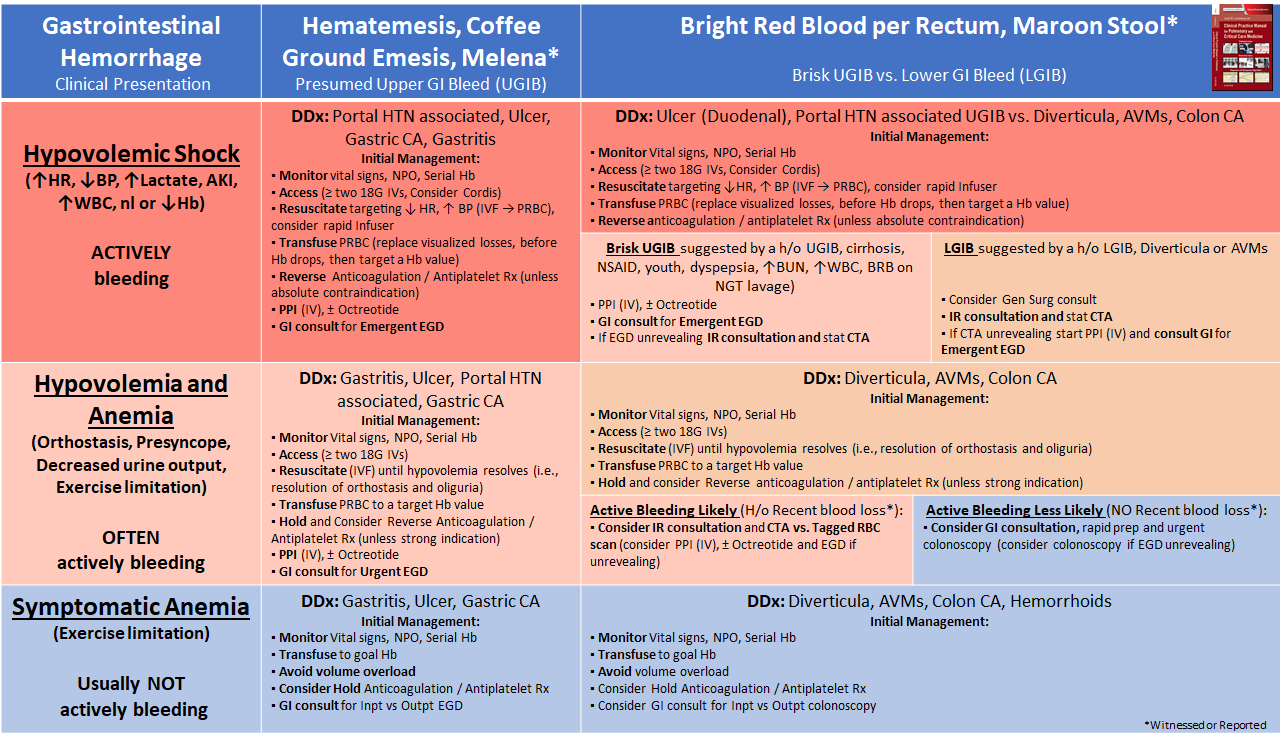
Treatment depends upon the severity of the volume loss. Summary hypovolemic shock happens when a drop in blood volume — usually due to bleeding — leads to severe complications, including organ failure. Rapid correction should be avoided to reduce.
And by preventing return of the available circulating blood volume to the legs. With hypotonic fluid (eg, 0.45% saline), even less remains in the vasculature, and, thus, this fluid is not used for resuscitation. Hypovolemia refers to a serious decrease in the amount of fluid in the body.
The physical exam will help determine if the patient has whole body fluid loss (e.g., dehydration in patients with renal disease), vascular space fluid loss (e.g., hypovolemia due to blood loss), or hypervolemia (e.g., heart disease, iatrogenic fluid overload). A pneumatic antishock garment counteracts bleeding and hypovolemia by slowing or stopping arterial bleeding; Treatment of hypovolemia depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms.





![[BKEYWORD03]](http://image2.slideserve.com/5098505/management-of-hypovolemic-shock-n.jpg)